Pregnancy & Diabetes Essential facts
Targets during pregnancy

Importance of blood glucose control in 1st trimester: First trimester is organ formation period. Baby is at risk for birth defects if mother’s blood glucose is not controlled. Hence it is must to have tight blood glucose control during 1st trimester.
Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): Testing blood glucose is essential during pregnancy. Frequency of testing ranges from 2-3 times daily to at least once in a week based on stability of blood glucose. Patient should adjust her insulin by 2 to 4 units based on SMBG report.
Pregnancy & diabetes drugs: So far as safety and flexibility are concerned Insulin is best treatment for diabetes during pregnancy. Insulin doesn’t cross placenta. Some oral drugs are proved safe during pregnancy but flexibility of dosage adjustment is limited.
Pregnancy and diabetic complications: Diabetic patient planning for pregnancy must get her eye testing and kidney testing done before and during pregnancy. Diabetic Retinopathy and Nephropathy (kidney disease) are known to get aggravated during pregnancy.
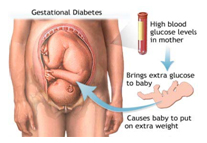
Baby of diabetic mother. If diabetes control is poor in 3rd trimester, chances of big sized baby (more than 4 kg weight) are high. Immediately after delivery big sized baby is at risk for low blood sugar, low calcium, jaundice, respiratory distress and many other complications. All these complications are preventable if mother’s blood glucose is under good control in last 3 months.
What will happen to diabetes after delivery? In 30% patients it disappears, in 30% it continues after delivery and in remaining patients it goes away after delivery but reappears in next pregnancy. Even if it disappears after delivery, it leaves a warning signal for future diabetes.






